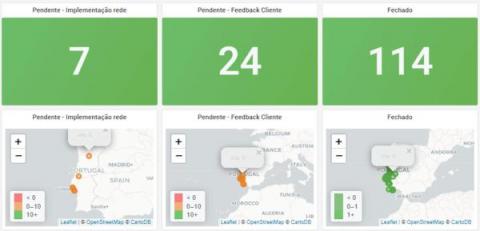
Troubleshoot in less than 60 seconds with Grafana: Inside NOS's observability stack
It may seem like ancient history, but there was a time when telecommunications companies only had to worry about connecting customers over landlines. Today, their businesses depend on vast cellular networks to not only provide strong wireless phone coverage in countless locations, but also handle the demands of tablets, computers, and machine-to-machine communications.