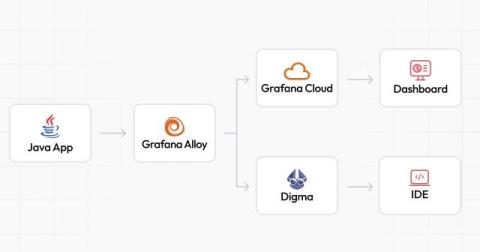
Three reasons why your business needs infrastructure monitoring
A business's website or application might appear polished on the surface, but if the underlying infrastructure is struggling, the user experience also suffers. Users can only benefit from applications and services if the critical back-end infrastructure is functional. Here's where infrastructure monitoring comes in—it acts as a watchful eye in your IT environment, ensuring everything runs smoothly.