Operations | Monitoring | ITSM | DevOps | Cloud
SIEM
Momma Said Grok You Out: Use LogStream to Streamline Searches, Aid in Reformatting Data and Parsing
It is commonly believed that once data is collected and ingested into a system of analysis, the most difficult part of obtaining the data is complete. However, in many cases, this is just the first step for the infrastructure and security operations teams expected to derive insights.
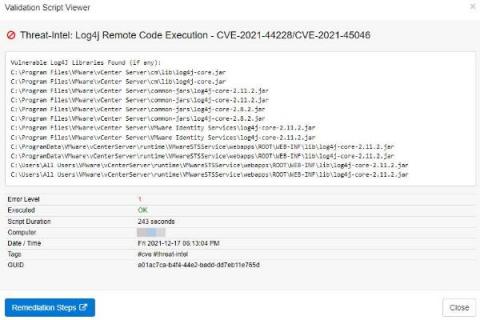
Discovering vulnerable Log4J libraries on your network with EventSentry
Just when the Microsoft Exchange exploit CVE-2021-26855 thought it would win the “Exploit of the year” award, it got unseated by the – still evolving – Log4J exploit just weeks before the end of the year! Had somebody asked Sysadmins in November what Log4J was then I suspect that the majority would have had no idea. It seems that the biggest challenge the Log4J exploit poses for Sysadmins is simply the fact that nobody knows all the places where Log4J is being used.
Managing Your SIEM EPS License with Cribl LogStream
We see unfriendly customer practices all around in the SIEM space. For example, some major SIEM vendors use an Events Per Second (EPS) license model to monetize access to their tools. Typically, these vendors will drop data above the EPS license or stop data ingestion to incentive license compliance if you run over your EPS license. These license controls disrupt operations and risk enterprise security posture, which can cause chaos.
JFrog Xray + Splunk + SIEM: Towards Implementing a Complete DevSecOps Strategy
Elastic Introduces the Industry's First Free and Open Limitless XDR
Why Cloud-Native SIEM?
The SIEM is a central point where data is collected and correlated, and as we move to consume more cloud services and data sets the SIEM itself must also change in architecture. Architecture change is hard to make for existing products. Calling a product a ‘cloud solution’ is not the same as taking an on-premises product and hosting it for customers. It means building a new SIEM for a new world. There are a lot of reasons users seek new SIEMs.
How Orange Business Services is building a better SIEM with Elastic
I’m a security analyst at Orange Business Services in Paris, and one of my current projects for the Orange Group is implementing a new SIEM based on the Elastic Stack. In this blog post, I’ll share why we chose Elastic and how we were able to integrate Elastic into our existing SIEM, resulting in faster investigations and saving our engineers’ time. So follow along.