Operations | Monitoring | ITSM | DevOps | Cloud
Vulnerability
Spotting Vulnerabilities at Rest and at Runtime feat. Cloudsmith and Sysdig
Unpatched Microsoft 0-Day: How to Mitigate CVE-2023-36884 with PowerShell
Microsoft's July 2023 Patch Tuesday updates highlighted several vulnerabilities under active exploitation, including one (or more?) that remains unpatched. Here's what you need to know about CVE-2023-36884, a zero-day vulnerability that attackers are exploiting to gain remote code execution via "specially-crafted" Microsoft Office documents.
Trusted Types: How we mitigate XSS threats in Grafana 10
Grafana is a rich platform for data visualization, giving you full control over how your data should be visualized. However, this flexibility and freedom comes with some challenges from a security perspective — challenges that need to be solved to protect the data in Grafana. For years, cross-site scripting (XSS) has been among the most common web application security vulnerabilities.
Managing security vulnerabilities and compliance for U.S. Government with Ubuntu Pro
New Apple Zero-Days: Patch CVE 2023-32434 and CVE 2023-32435
How IT Device Discovery Can Identify Your Network's Assets and Vulnerabilities
The security of your organization’s network is paramount to its success. With the ever-changing landscape of cyber threats, it's important to take the necessary steps to ensure that your network is secure and compliant with industry regulations. Ensuring compliance requires you to know what’s on your network. But how can that be done when only 48% of leaders and security professionals say they run their asset discovery program at least once per week?
How Implementing Risk-Based Patch Management Prioritizes Active Exploits
Resistance to change is always present, especially if you think the processes you have in place are efficient and effective. Many organizations feel this way about their software management procedures until they have a security breach or incident and are left wondering where they went wrong. The reality is that most patch management programs are built on assumptions and recommendations, rather than facts about actively exploited vulnerabilities. Risk-based patch management is the answer to this issue.
What is so Pro in Ubuntu Pro?
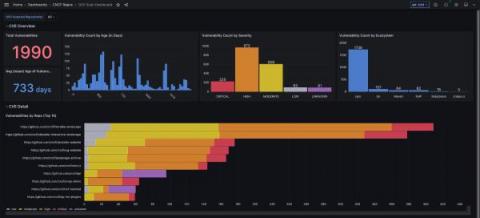
How to manage CVE security vulnerabilities with Grafana, MergeStat, and OSV-Scanner
Patrick DeVivo is a software engineer and founder of MergeStat, an open source project that makes it possible to query the contents, history, and metadata of source code with SQL. The security posture of software supply chains has been a significant topic lately. Recent high-profile breaches have shown the importance of managing risks from third party code. Take, for example, the Log4Shell vulnerability (tracked as CVE-2021-44228 — Grafana Labs was not affected).