How to Analyze Workplace Search Usage in Kibana
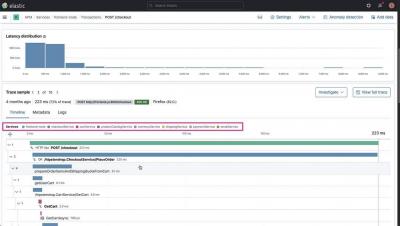
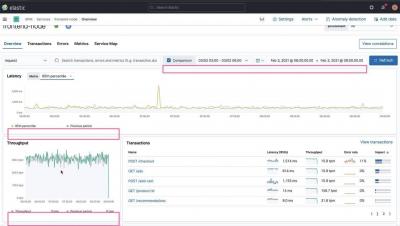
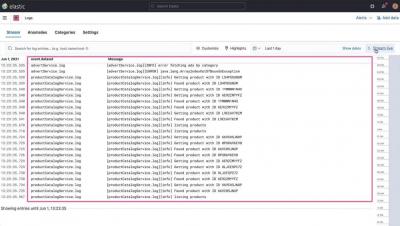
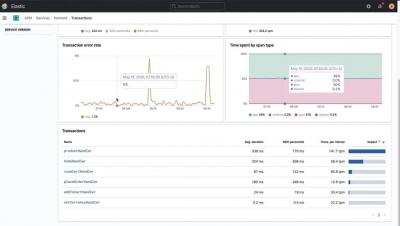
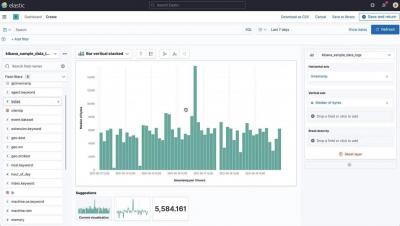
Elastic Workplace Search collects and stores product usage data, which you can use to create helpful visualizations and gain insight into what your users are searching for. In this video, you’ll learn how to leverage this data by building a dashboard in Kibana using Lens.