Operations | Monitoring | ITSM | DevOps | Cloud
Latest Posts
2024 Is the Year of Software Delivery Reinvented
Progressive Delivery for Stateful Services Using Argo Rollouts
New CNCF Survey Highlights GitOps Adoption Trends - 91% of Respondents Are Already Onboard
Introducing GitOps Versions: A Unified Way to Version Your Argo CD Applications
Last month, we announced our new GitOps Environment dashboard that finally allows you to promote Argo CD applications easily between different environments.
Introducing Products: A Tool to Model Argo CD Application Relationships and Promotions
At Codefresh, we are always happy to see companies and organizations as they adopt Argo CD and get all the benefits of GitOps. But as they grow we see a common pattern: It is at this point that organizations come to Codefresh and ask how we can help them scale out the Argo CD (and sometimes Argo Rollouts) initiative in the organization. After talking with them about the blockers, we almost always find the same root cause.
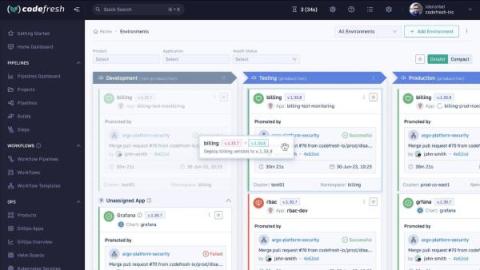
Introducing the World's First Dashboard for GitOps Environments
Defining multiple environments in Argo CD and promoting an application between them is one of most popular questions for companies that adopt GitOps for their applications. While we have offered several guidelines in the past for organizing your GitOps environments, today we are taking it further by announcing a complete product that helps you visualize the full lifecycle of an application as it moves through different stages. Meet the new Codefresh GitOps Environment Dashboard!
Using Helm and Terraform for Codefresh Gitops Installations
Last year we launched the Codefresh delivery platform powered by Argo. After the initial launch we started collecting feedback from all companies that tried it (as well as existing customers) and cataloged all feature requests and implementation ideas. The main goal is always to iterate quickly and address the most common issues in the most efficient way possible.
Multi-Service Progressive Delivery with Argo Rollouts
In the previous article of the series, we explained how to use Configmap generators in order to use Progressive Delivery for your configuration (and not just the container images). In this post, we will also cover another popular question: how to use Argo Rollouts with multiple services. Argo Rollouts is a Kubernetes controller that allows you to perform advanced deployment methods in a Kubernetes cluster. By default, it only supports a single service/application.
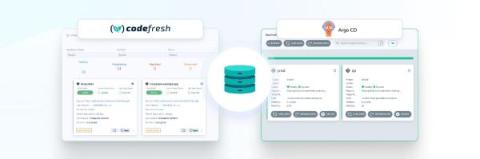
Using GitOps for Databases
In our previous article about Database migrations we explained why you should treat your databases with the same respect as your application source code. Database migrations should be fully automated and handled in a similar manner to applications (including history, rollbacks, traceability etc).