Operations | Monitoring | ITSM | DevOps | Cloud
January 2022
[Infographic] AWS Elastic Load Balancing from a Serverless perspective
Load balancing is a significant part of every internet-facing software, and with Elastic Load Balancing (ELB), AWS offers a set of load balancers for every use case. Since our latest update, Dashbird also gives you insights into these ELB services; let’s look at them and see how they can be used in a serverless environment.
Designing production-ready AWS serverless applications
Serverless has become an increasingly popular paradigm among organizations looking to modernize their applications as it allows them to increase agility while reducing their operational overhead and costs. But the highly distributed nature of serverless architectures requires developers to rethink their approach to application design and development. AWS-based serverless applications hinge on AWS Lambda functions, which are stateless and ephemeral by design.
Azure Service Bus Logging with BAM - Walk-through
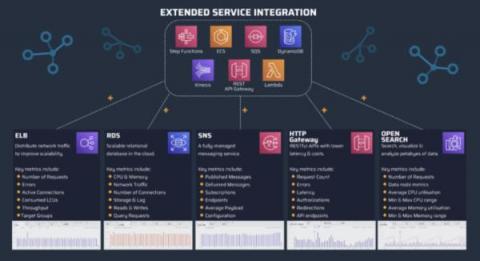
Dashbird now integrates with 5 new AWS services
TL;DR: Dashbird launches observability for five new AWS services (ELB, SNS, RDS, OpenSearch, and HTTP API Gateway) to allow for a faster, more secure, and smoother serverless observability experience. Dashbird, the leading monitoring platform for serverless AWS applications, announces five new AWS integrations.
What is an AWS Lambda Function?
In this article, we will cover the basics of a Lambda function and its functionality in our every day digital lives. AWS Lambda, as we already know, is a compute service that allows you to run code without managing servers. AWS Lambda runs the code when it is needed, and it is automatically scaled. The code you execute on AWS Lambda is called Lambda function, and it can be considered, for better understanding, as a formula in a spreadsheet.
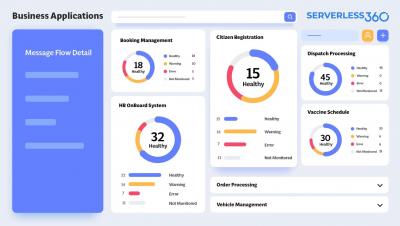
Feature Spotlight - Business Applications
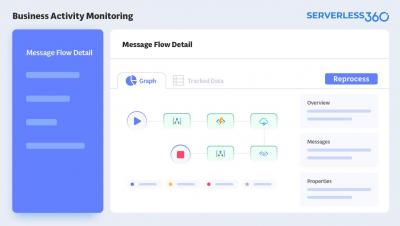
Feature Spotlight - Business Activity Monitoring
Feature Spotlight - Azure Documenter
Easy Lambda Function Monitoring with the AWS Lambda InfluxDB Template
AWS Lambda is a serverless compute service that allows you to run code without having to manage servers. Lambda provides autoscaling and bills only on compute time, so you aren’t paying for unused resources. Some common use cases are file processing, stream processing, and acting as a backend for web and mobile applications. AWS Lambda functions can be invoked with external HTTP requests as well as by events triggered by over 200 different AWS services.