Operations | Monitoring | ITSM | DevOps | Cloud
Latest Posts
Data Lakehouses Explained
A Guide to Predictive Maintenance & Machine Learning
Grafana Dashboard Tutorial: How to Get Started
Data lakes vs data warehouses explained
Mage for Anomaly detection with InfluxDB and Half-space Trees
Any existing InfluxDB user will notice that InfluxDB underwent a transformation with the release of InfluxDB 3.0. InfluxDB v3 provides 45x better write throughput and has 5-25x faster queries compared to previous versions of InfluxDB.
Bringing it all together: Speed, performance, and efficiency in InfluxDB 3.0
For most of the past year, we here at InfluxData focused on shipping the latest version of InfluxDB. To date, we launched three commercial products (InfluxDB Cloud Serverless, InfluxDB Cloud Dedicated, and InfluxDB Clustered), with more open source options on the way. All the while, we claimed that this latest version of InfluxDB surpasses anything we built before.
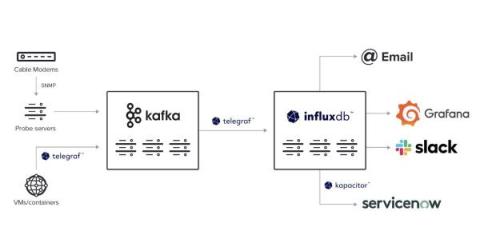
How WOW! Modernized Legacy Infrastructure Monitoring with InfluxDB and Kafka
With over 500,000 residential, business, and wholesale customers across multiple markets in the United States, WideOpenWest (WOW!) is one of the United States’ largest broadband providers. They aim to connect homes and businesses to the world with fast and reliable internet, TV, and phone services.
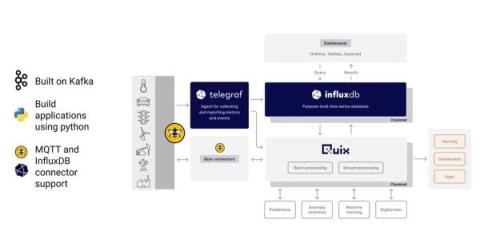
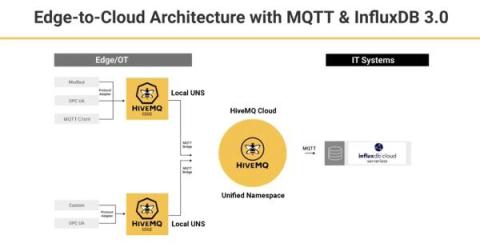
Webinar Recap: Build an Edge-to-Cloud Architecture Using MQTT and InfluxDB
Industrial IoT (IIoT) machines and sensors generate valuable time series data. It’s impossible to derive the insights necessary to inform decisions as a company to produce or operate more efficiently without sending operational technology (OT) data to informational technology (IT) systems.
Querying Arrow tables with DataFusion in Python
InfluxDB v3 allows users to write data at a rate of 4.3 million points per second. However, an incredibly fast ingest rate like this is meaningless without the ability to query that data. Apache DataFusion is an “extensible query execution framework, written in Rust, that uses Apache Arrow as its in-memory format.” It enables 5–25x faster query responses across a broad range of query types compared to previous versions of InfluxDB that didn’t use the Apache ecosystem.