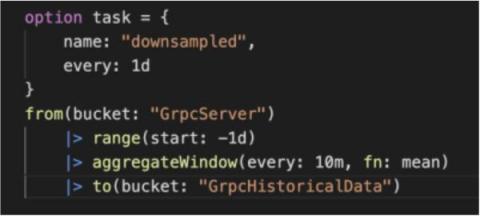
Backfill Missing Time Series With SQL
Time series data streams are often noisy and irregular. But it doesn’t matter if the cause of the irregularity is a network error, jittery sensor, or power outage – advanced analytical tools, machine learning, and artificial intelligence models require their data inputs to include data sets with fixed time intervals. This makes the process of filling in all missing rows and values a necessary part of the data cleaning and basic analysis process.