Operations | Monitoring | ITSM | DevOps | Cloud
StackState
Time-traveling topology in observability w/ Mark Bakker and Lodewijk Bogaards | The StackPod EP #1
Save 85% in Time Spent on Root Cause Analysis with Topology-based Observability | StackState demo
How it all began... - StackState's origin story
It’s 2014. A major Dutch bank is struggling with performance problems in highly visible customer-facing applications. These performance problems are proving to be incredibly difficult to resolve. It’s not that there’s no monitoring data that could potentially help. In fact, there’s tons of it, all nicely displayed in pretty dashboard after pretty dashboard.
Elastic and StackState Team Up to Pull Needles Out of Haystacks
Delivering great performance and reliability for your critical applications just keeps getting harder, doesn’t it? Between microservices, mercurial cloud resources, containers spinning up and down, distributed teams, specialized teams, and developers making changes, it’s an increasingly complex environment. With so many moving parts, if something goes wrong, how do you know what happened where, and what your environment looked like at the precise moment the problem began?
The Ultimate Guide To Telemetry
If you’re anywhere in the Queensland region of northern Australia, look out. There’s an eight-foot-nine-inch-long (2.65 meters) crocodile, deceptively named Danny-Boy, who might be looking for a snack. Specifically, if you’re anywhere near -12.975388, 141.987344, you should stay on your toes. That’s the last place Danny-Boy was sighted. So unless you want your pipes to be calling, keep your eyes peeled.
How to get started with StackState's cloud observability platform
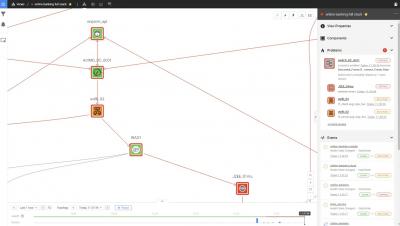
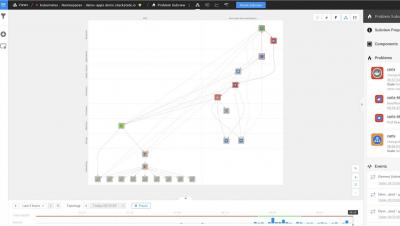
Investigating the Scene of an Incident: Using a Time-Traveling Topology to Create Escalation Graphs
Yes, time travel is possible...through data. My ability to time travel began when I started coding at age 10. Back then, all of my code ran on my own little computer. Like many ten-year-olds, I coded to create and play games. I also coded cool graphics to accompany music to impress my friends and utilities for copying. I launched my first commercial website in 1996 and made 25 guilders, which was good money for a 15-year old. Life was so easy.
Observability and the Monitoring Maturity Model
In incident management, observability is the ability of an organization or team to infer a system's internal state from its external outputs.