HoneyByte: Make a Beeline Toward Observability Just Like DEV's Molly Struve
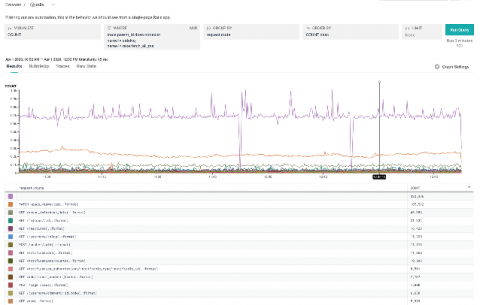
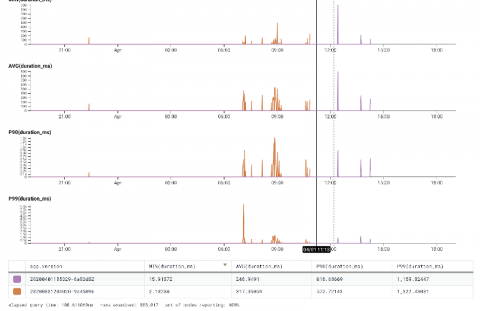
“When things broke,” Molly explained, “you’re mad scrambling—jumping from website to website to website, trying to put the pieces together.” Molly was able to use Honeycomb to fix things up: “It makes my job easier as an SRE.” Getting started with Honeycomb doesn’t require a lot of work: at dev.to, they used the Ruby Beeline to get it going: “I didn’t do that much,” she said.